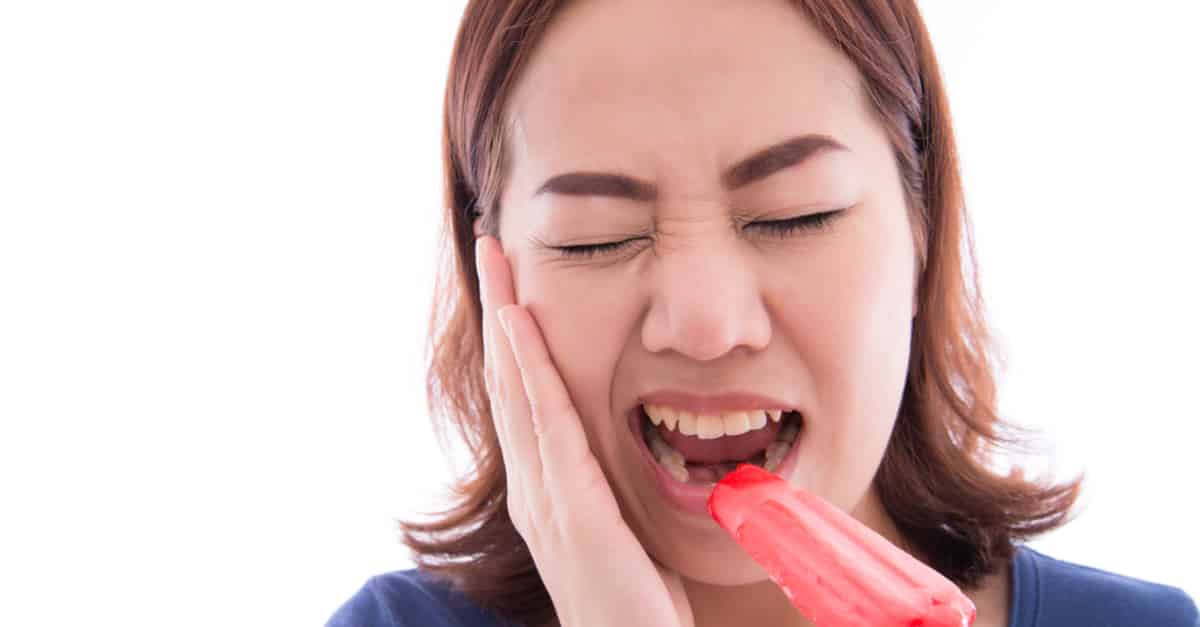

What causes tooth sensitivity?
If you experience a sharp, sudden pain when enjoying hot coffee, cold ice cream, or even brushing your teeth, you’re not alone. Tooth sensitivity affects millions of people and can range from mildly uncomfortable to quite painful. But what exactly causes this sensitivity?
Understanding Tooth Sensitivity
Tooth sensitivity, also known as dentin hypersensitivity, happens when the protective layers of your teeth are compromised. Normally, your enamel—the hard outer layer—protects the softer dentin beneath it. The dentin contains tiny tubules that lead to nerve endings inside the tooth. When enamel wears away or gums recede, these tubules become exposed, allowing stimuli like temperature changes or acidic foods to trigger pain.
Common Causes of Tooth Sensitivity
-
Enamel Erosion: Acidic foods and drinks (like citrus fruits, soda, or wine), aggressive brushing, or teeth grinding (bruxism) can wear down enamel over time.
-
Gum Recession: When gums pull back from the teeth, the exposed root surfaces (which are not covered by enamel) become sensitive.
-
Tooth Decay or Cavities: Cavities expose the dentin or pulp, causing sensitivity and pain.
-
Cracked or Chipped Teeth: Damage to a tooth can expose the underlying dentin or nerves.
-
Recent Dental Procedures: Treatments like fillings, teeth whitening, or cleanings can temporarily increase sensitivity.
-
Use of Whitening Products: Some whitening treatments can cause temporary sensitivity.
-
Plaque Buildup: Excess plaque near the gumline can cause sensitivity by irritating the gums.
How to Manage Tooth Sensitivity
-
Use Desensitizing Toothpaste: These toothpastes contain compounds that help block pain signals from the tooth surface to the nerve.
-
Avoid Acidic Foods and Drinks: Limit consumption of acidic substances and rinse your mouth with water afterward.
-
Gentle Brushing: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and avoid aggressive brushing.
-
Good Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing and flossing help prevent gum disease and decay.
-
Visit Your Dentist: If sensitivity persists, your dentist can diagnose the cause and recommend treatments such as fluoride varnishes, dental bonding, or gum grafts.
When to See a Dentist
If your tooth sensitivity is severe, lasts more than a few weeks, or is accompanied by other symptoms like swelling, pain when biting, or visible damage, it’s important to see your dentist promptly.
Final Thoughts
Tooth sensitivity is a common issue but can usually be managed effectively with the right care. Understanding the causes helps you protect your teeth and enjoy your favorite foods and drinks without discomfort.
Tag: doctor, medicinePopular Posts
-
-
How often should I visit the dentist?
05 Jun, 2025 -

-

-

What are the most common causes of bad breath?
05 Jun, 2025 -

Is mouthwash necessary, or is brushing enough?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Is teeth whitening safe?
05 Jun, 2025 -
What are dental veneers, and how do they work?
05 Jun, 2025 -
What's the difference between braces and Invisalign?
05 Jun, 2025 -

-
Can gum disease be reversed?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Why do my gums bleed when I brush or floss?
05 Jun, 2025 -
What happens if I ignore a cavity?
05 Jun, 2025 -
What is a dental implant, and how does it work?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Am I a good candidate for dental implants?
05 Jun, 2025 -
What should I expect after a tooth extraction?
05 Jun, 2025 -
What is dry socket, and how can I prevent it?
05 Jun, 2025 -
What causes receding gums?
05 Jun, 2025 -

What is bruxism, and how is it treated?
05 Jun, 2025 -

Is it safe to visit the dentist during pregnancy?
05 Jun, 2025 -
What is fluoride, and is it safe?
05 Jun, 2025 -
-

How does diet affect my oral health?
05 Jun, 2025 -

Why do my teeth hurt when I eat cold or hot foods?
05 Jun, 2025 -
What is plaque, and how do I get rid of it?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Are dental X-rays safe?
05 Jun, 2025 -
What’s the difference between a crown and a filling?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Can poor oral health affect my overall health?
05 Jun, 2025 -
What are sealants, and who needs them?
05 Jun, 2025 -
How long do dental implants last?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Is getting a dental implant painful?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Can anyone get dental implants?
05 Jun, 2025 -
How does a dental implant compare to a bridge?
05 Jun, 2025 -
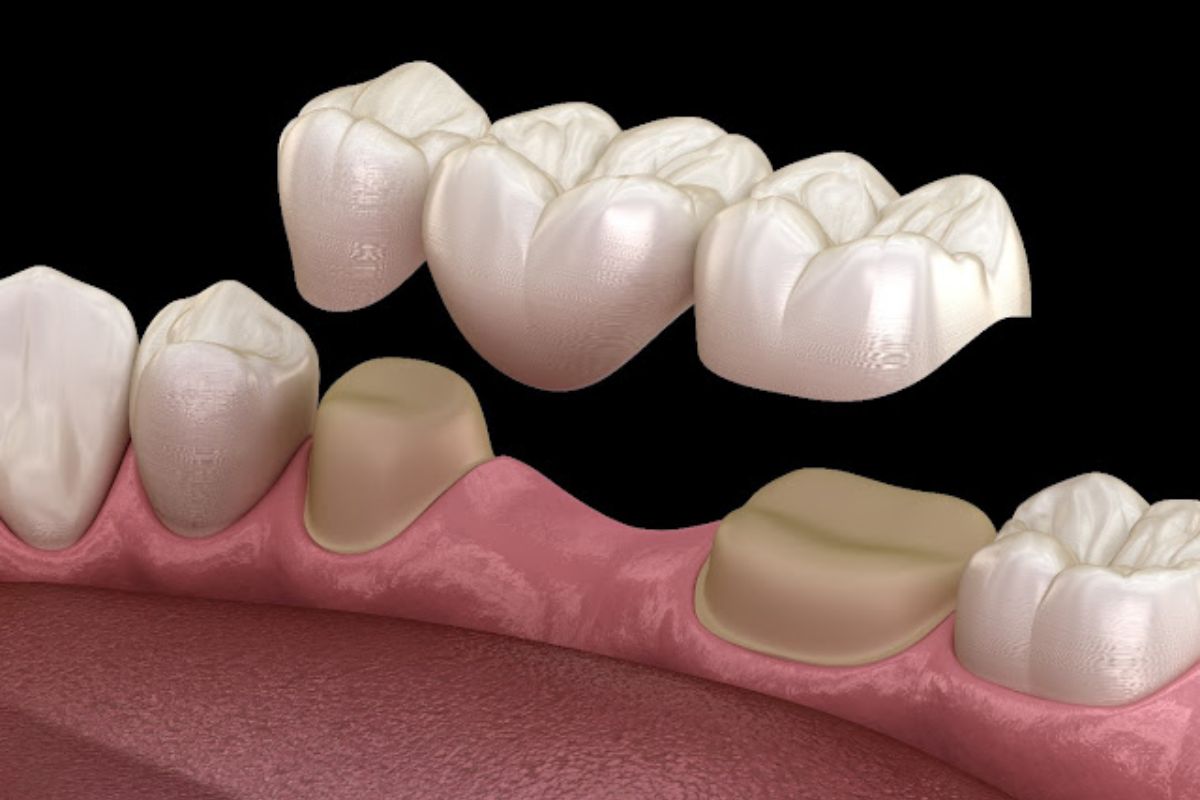
What is a dental bridge?
05 Jun, 2025 -
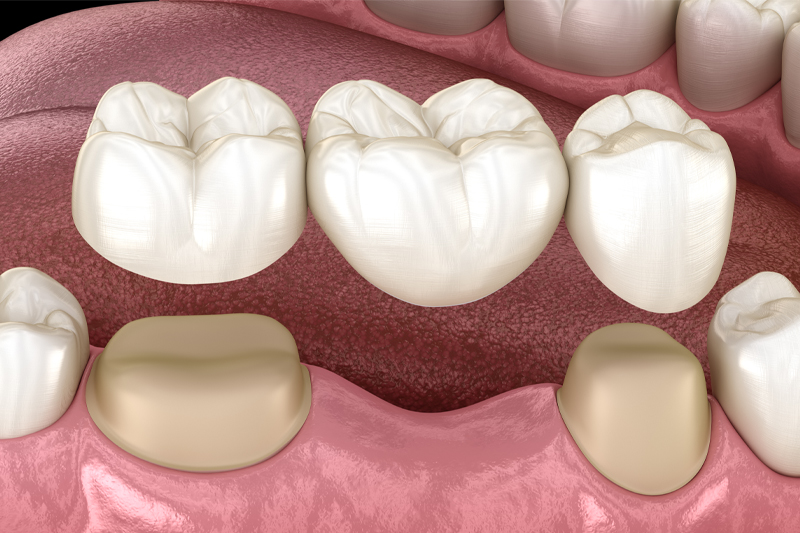
How long do dental bridges last?
05 Jun, 2025 -
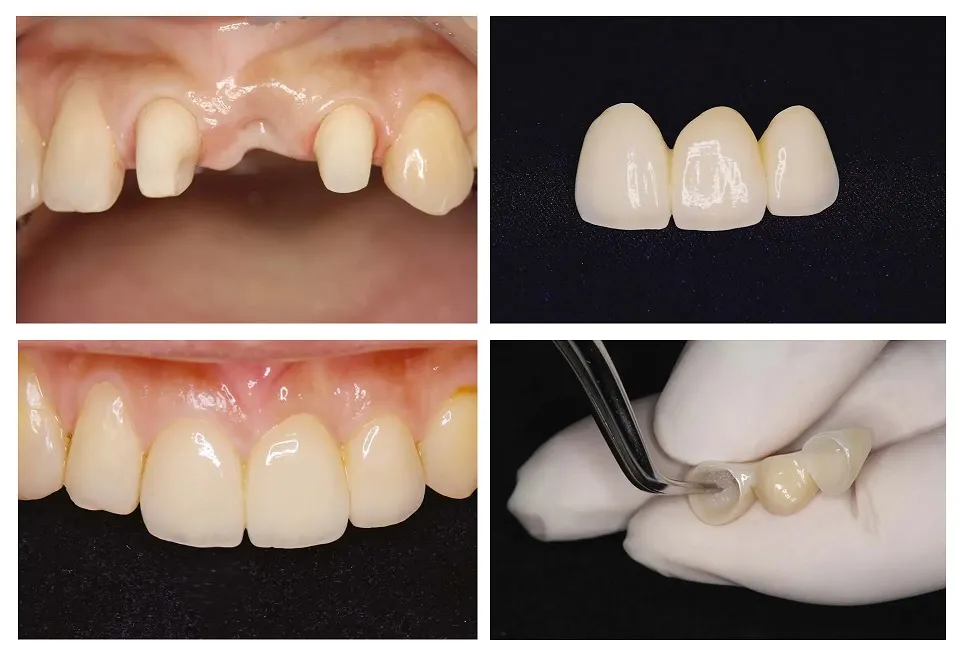
Are dental bridges noticeable?
05 Jun, 2025 -
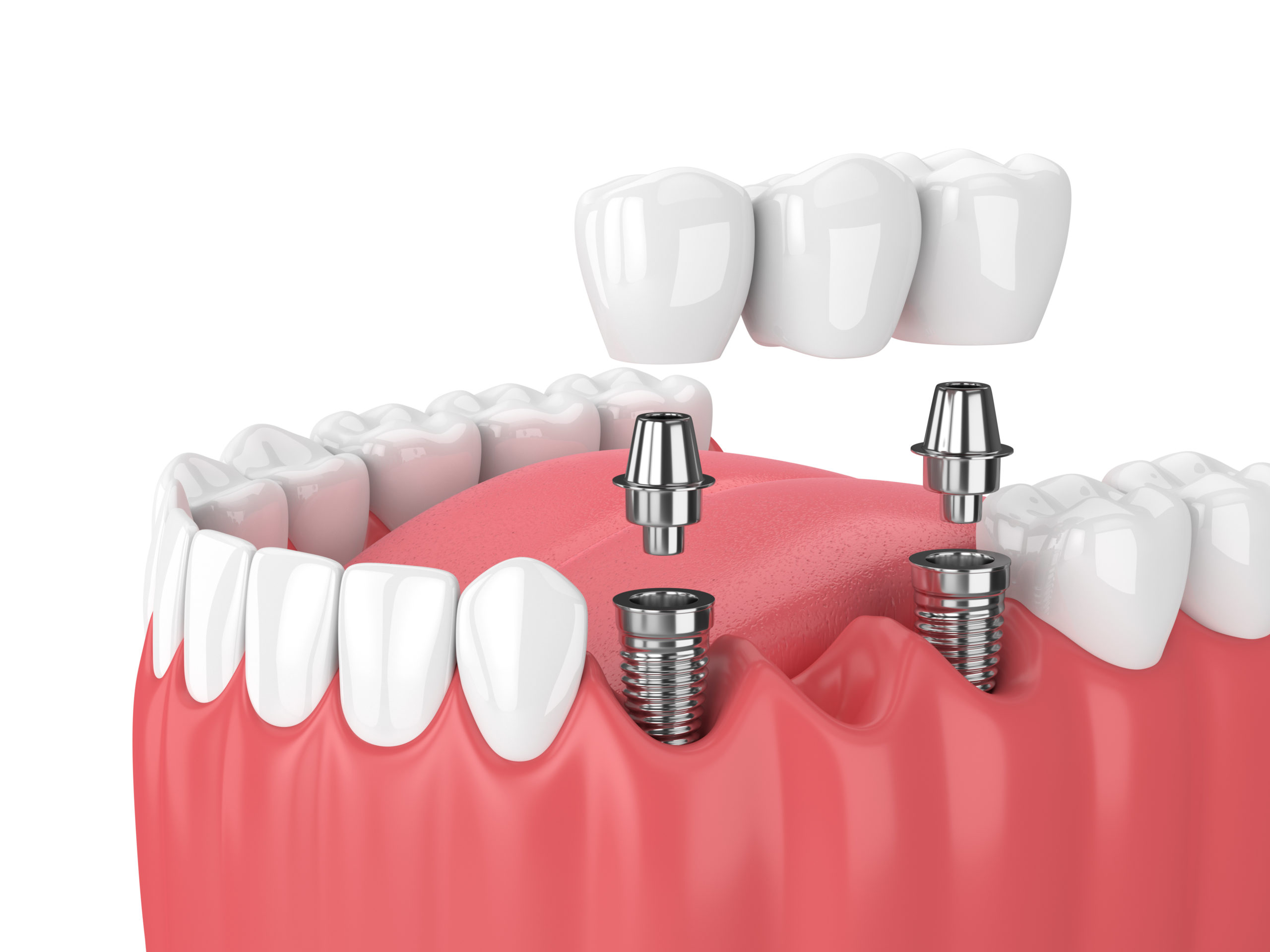
Can a bridge replace multiple missing teeth?
05 Jun, 2025 -
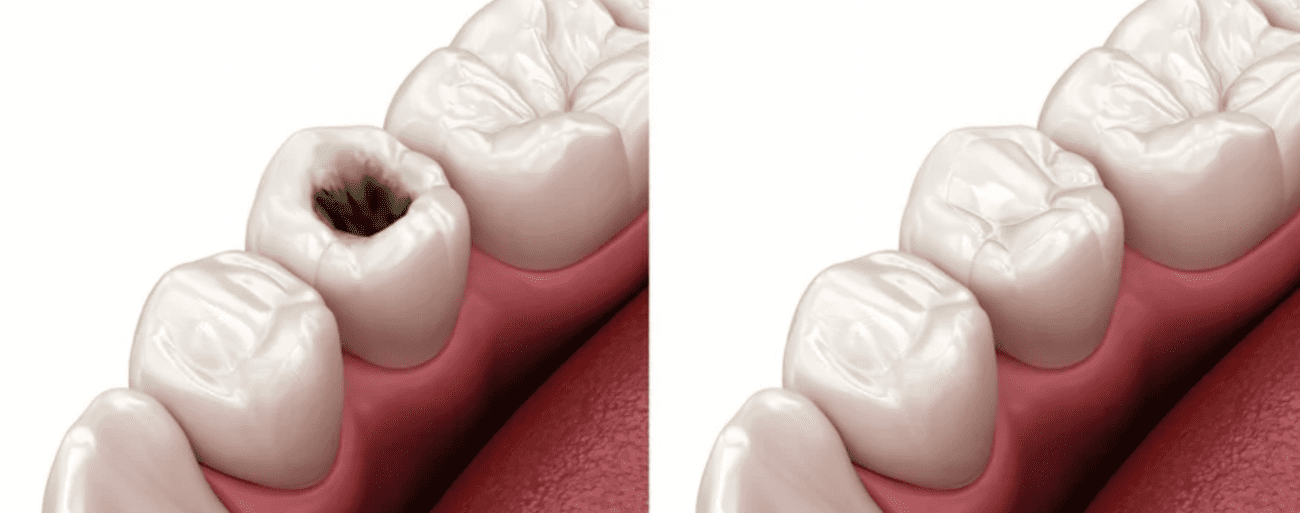
What is a dental filling and why is it needed?
05 Jun, 2025 -
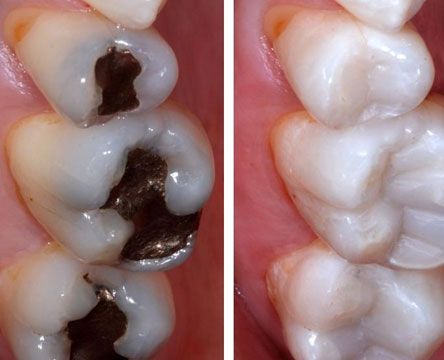
What types of materials are used for fillings?
05 Jun, 2025 -
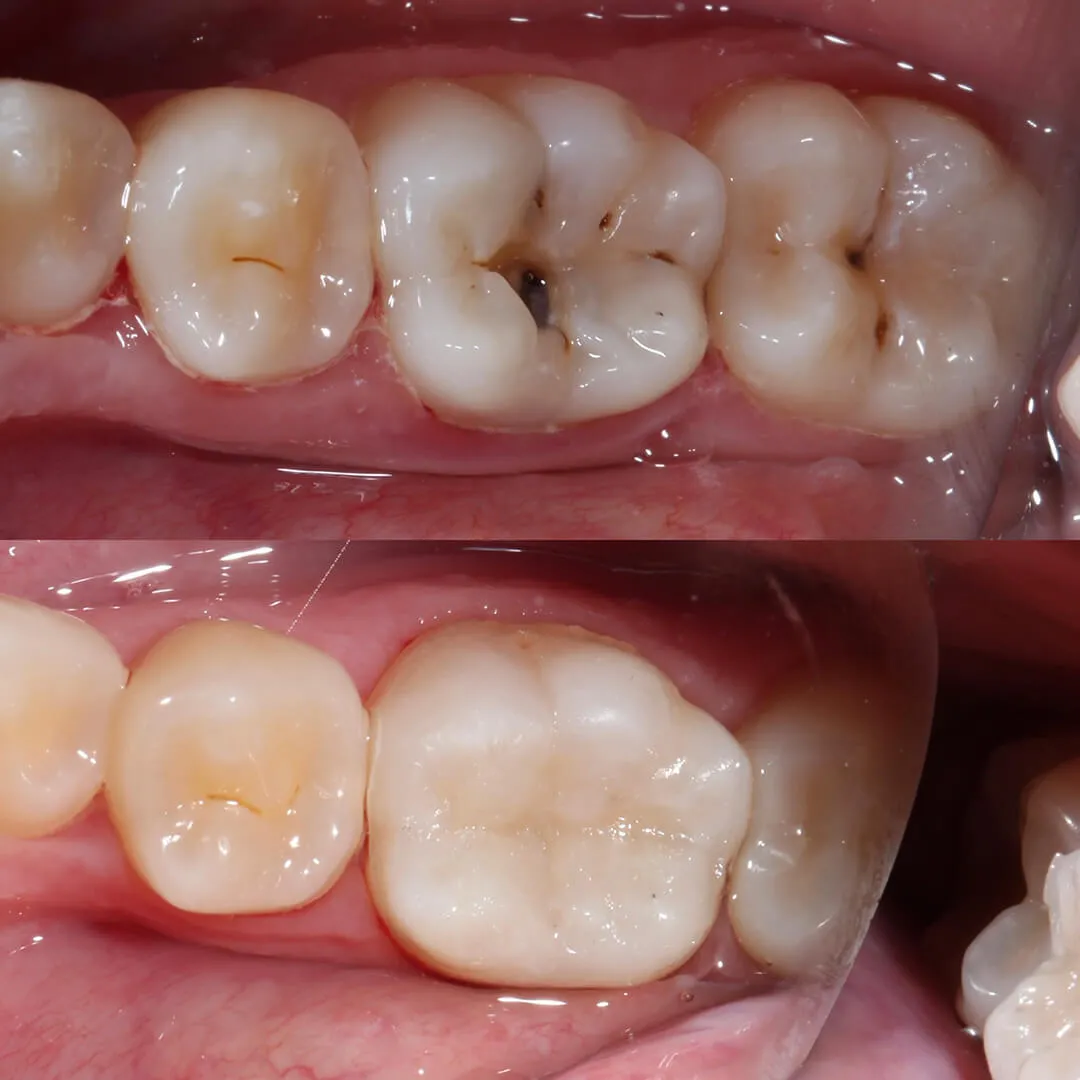
How long does a filling last?
05 Jun, 2025 -
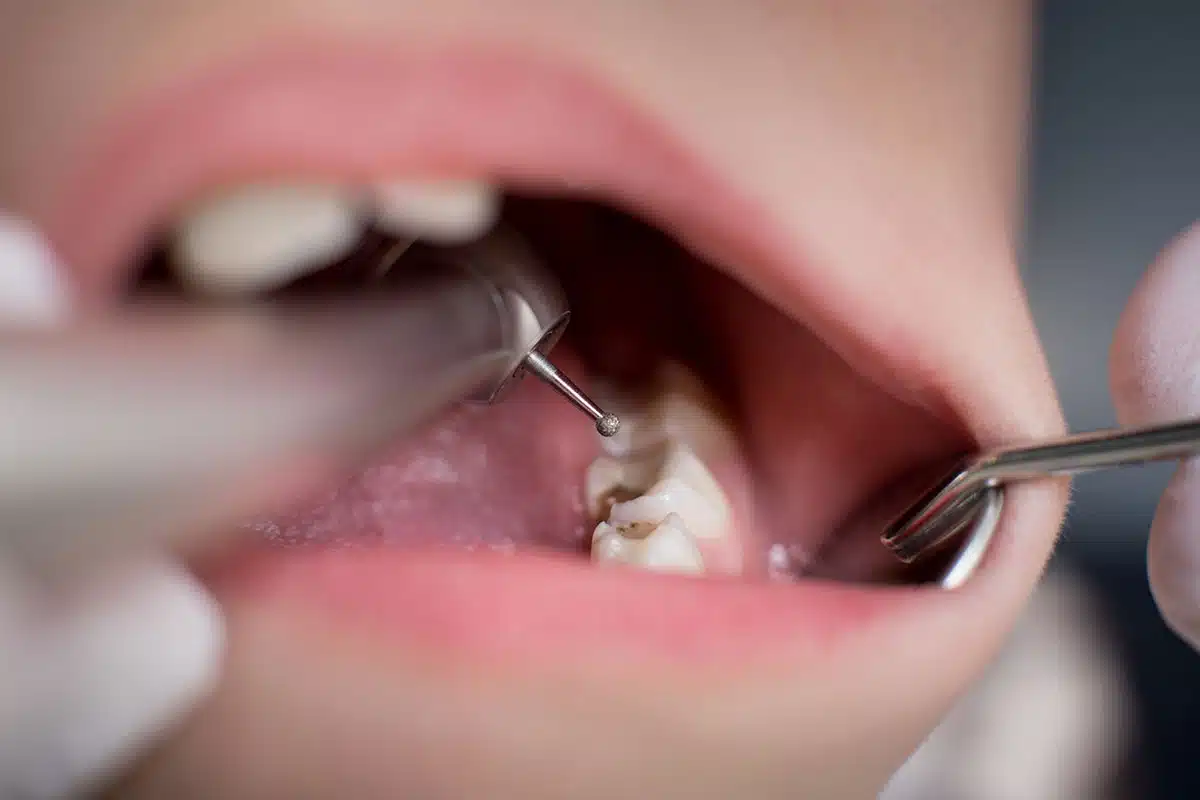
Is the filling procedure painful?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Can fillings fall out or break?
05 Jun, 2025 -
What is a root canal treatment?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Does a root canal hurt?
05 Jun, 2025 -

How do I know if I need a root canal?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Is the tooth dead after a root canal?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Why is a crown needed after a root canal?
05 Jun, 2025 -
What is cosmetic dentistry?
05 Jun, 2025 -
How long does teeth whitening last?
05 Jun, 2025 -
What’s the difference between bonding and veneers?
05 Jun, 2025 -
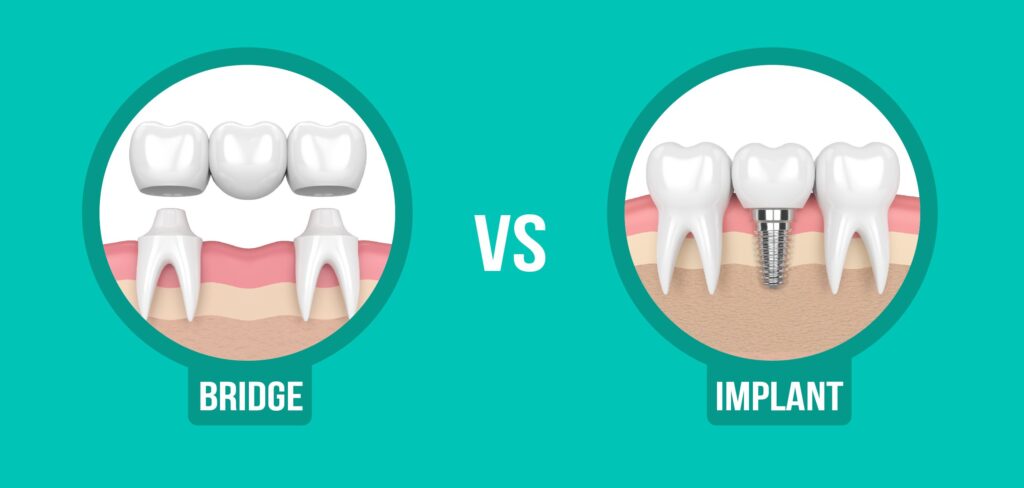
Is a dental implant better than a bridge?
05 Jun, 2025 -
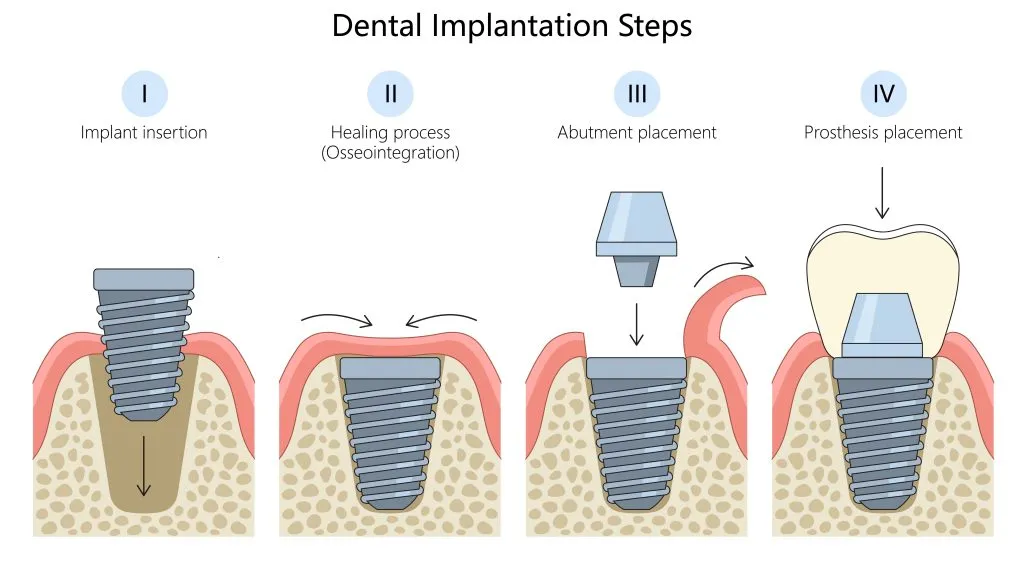
-
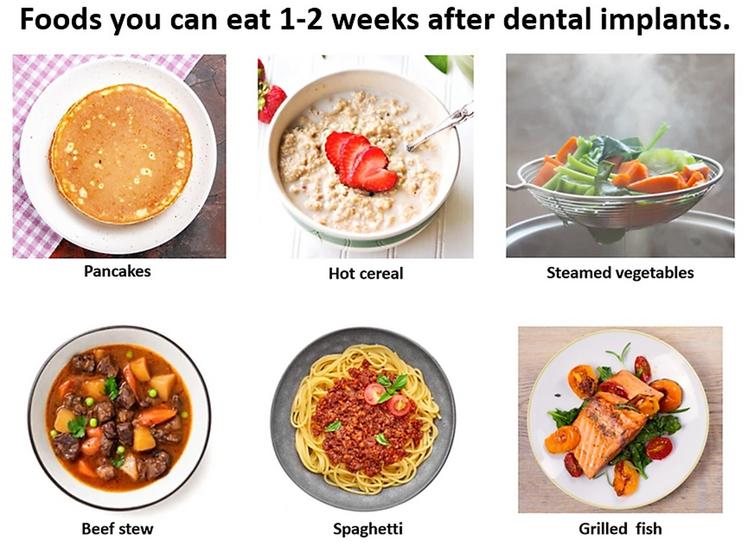
Will I be able to eat normally with dental implants?
05 Jun, 2025 -
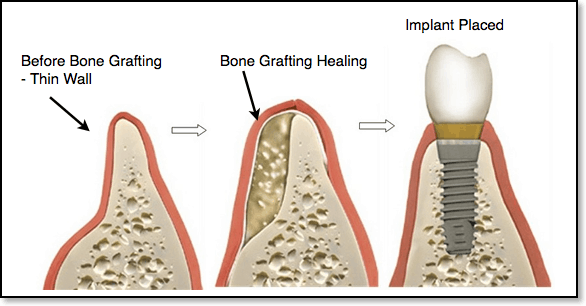
Is bone grafting always needed for implants?
05 Jun, 2025 -
-
Do fillings hurt after they’re placed?
05 Jun, 2025 -
How do I know if I need a filling?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Can children get tooth-colored fillings too?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Do I need a bridge if I’m missing just one tooth?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Can a bridge feel like a natural tooth?
05 Jun, 2025 -
How do I clean around a dental bridge?
05 Jun, 2025 -

Can I eat normally with a dental bridge?
05 Jun, 2025 -
How long does a root canal procedure take?
05 Jun, 2025 -
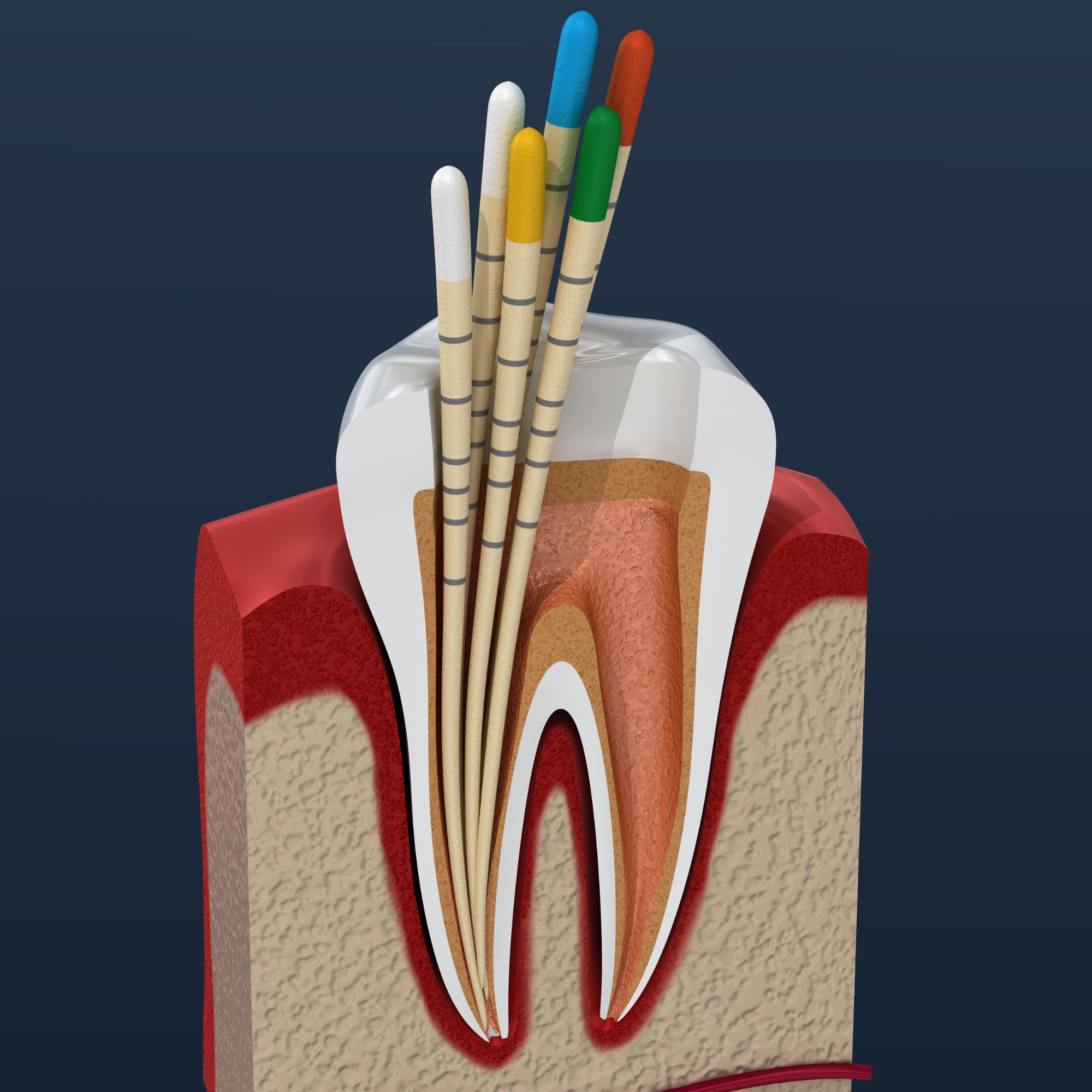
What happens after a root canal?
05 Jun, 2025 -
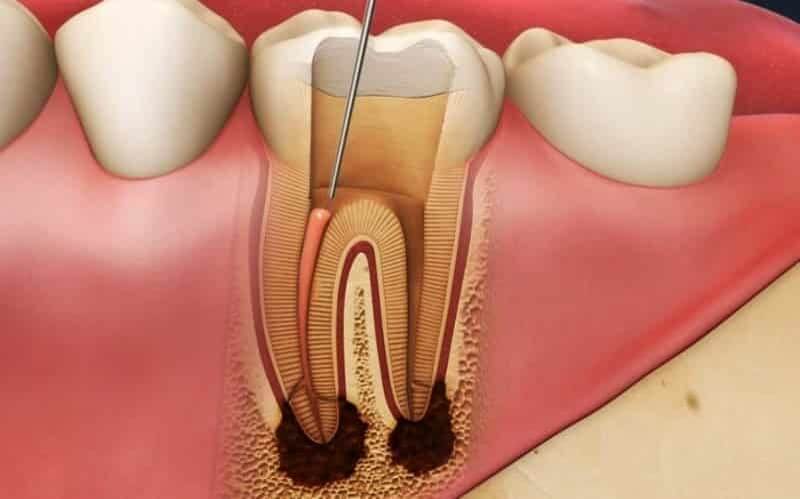
Can a root canal fail?
05 Jun, 2025 -

Is cosmetic dentistry only about appearance?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Can cosmetic dentistry fix gaps between teeth?
05 Jun, 2025 -

Are veneers permanent?
05 Jun, 2025 -
-
Will I be awake during my dental procedure?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Is dental anesthesia safe?
05 Jun, 2025 -
What are the side effects of dental anesthesia?
05 Jun, 2025 -

Can children safely receive dental anesthesia?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Do I need to be asleep for tooth extraction?
05 Jun, 2025 -
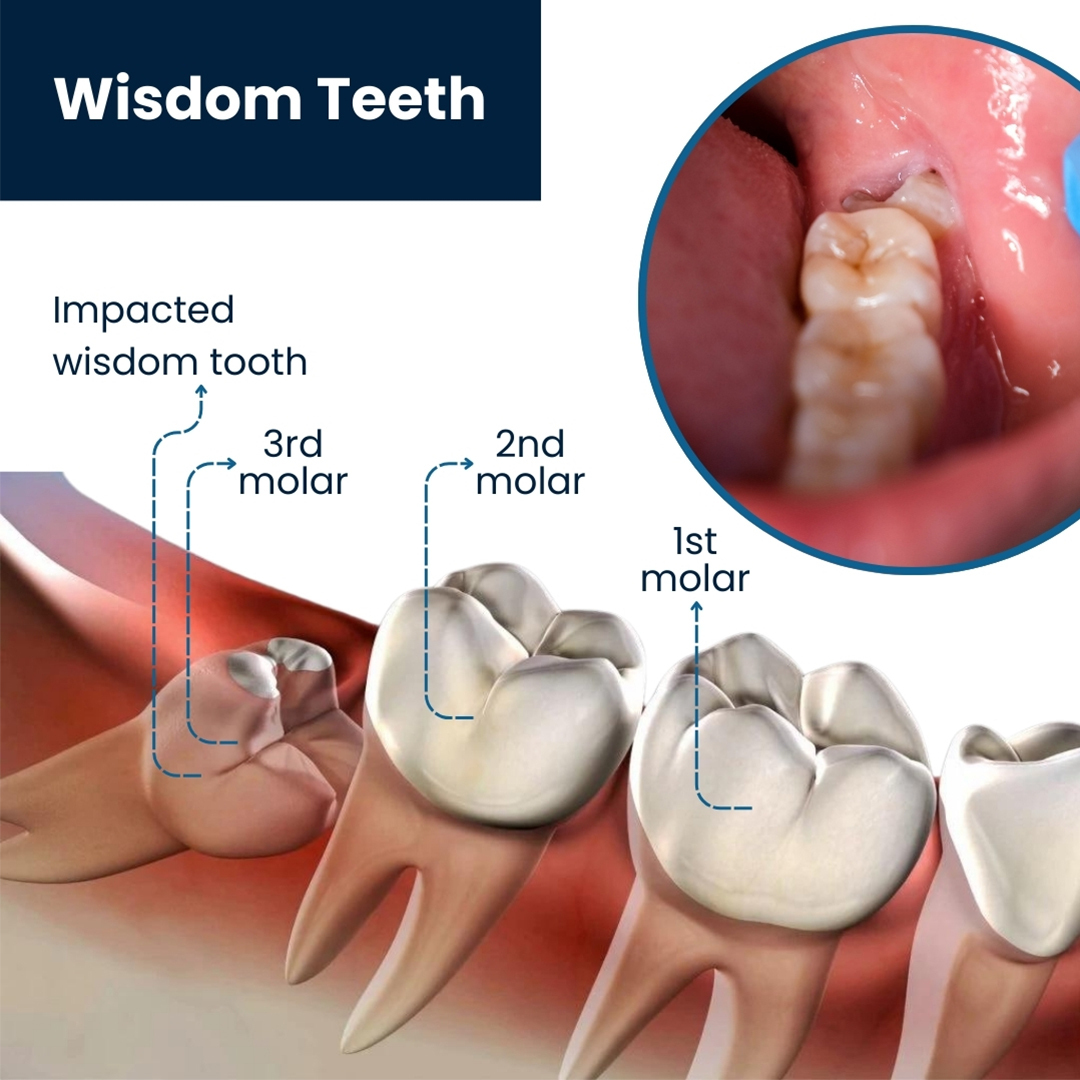
What are impacted wisdom teeth?
05 Jun, 2025 -
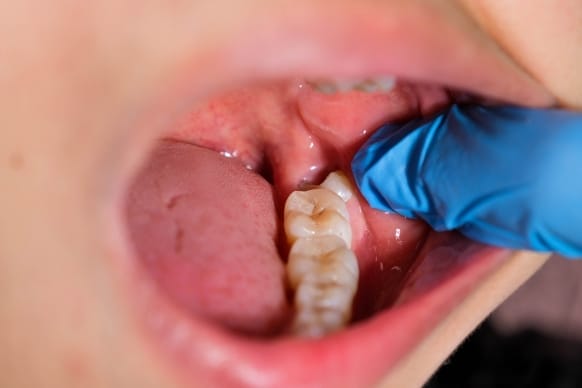
How long is the recovery after wisdom tooth surgery?
05 Jun, 2025 -
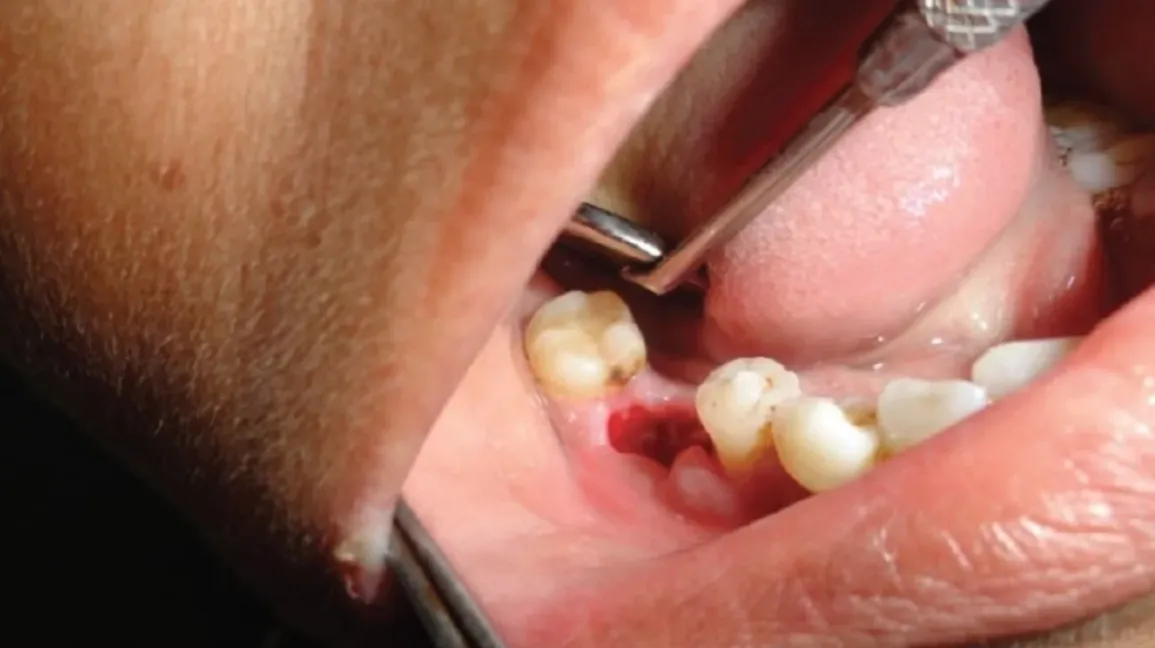
What is dry socket, and how can I avoid it?
05 Jun, 2025 -
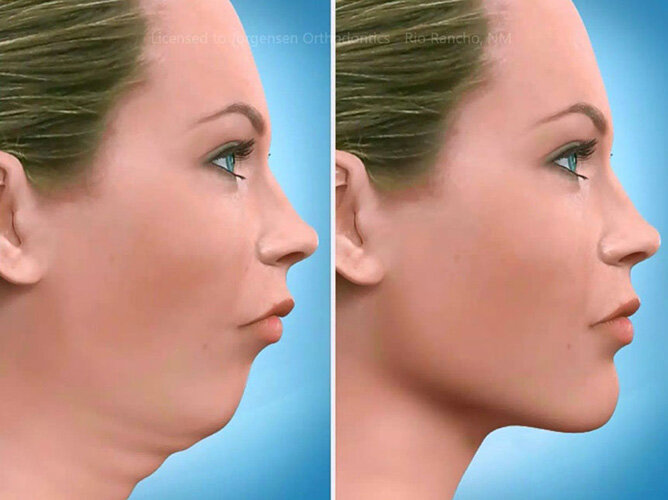
Is jaw surgery only for cosmetic reasons?
05 Jun, 2025 -
What is bone grafting in dentistry?
05 Jun, 2025 -

How painful is oral surgery?
05 Jun, 2025 -

Can I work the day after oral surgery?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Is oral surgery safe?
05 Jun, 2025 -

At what age should my child see an orthodontist?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Do braces hurt?
05 Jun, 2025 -
How long does orthodontic treatment usually take?
05 Jun, 2025 -
-

Can adults get braces too?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Will I need to wear a retainer after braces?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Can orthodontics fix jaw alignment problems?
05 Jun, 2025 -
How do I clean my teeth with braces?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Are there risks to orthodontic treatment?
05 Jun, 2025 -

Where is Balkan Dental Polyclinic located?
05 Jun, 2025 -

-

Do you offer travel or accommodation assistance?
05 Jun, 2025 -
Is English spoken at your clinic?
05 Jun, 2025 -

-

-
Can I get veneers in just one trip?
05 Jun, 2025 -

What if I need follow-up care after returning home?
05 Jun, 2025 -

-
-
How can I get a treatment plan before traveling?
05 Jun, 2025 -

What payment options are available?
05 Jun, 2025 -

-

Is dental care in North Macedonia safe and hygienic?
05 Jun, 2025 -

Are your dentists internationally trained?
05 Jun, 2025 -
-

Do you offer written warranties for treatments?
05 Jun, 2025 -
